1) current
[英]['kʌrənt] [美]['kɝənt]


电流
1.
Experiments on Effects of M-EMS Current on Quality of Bloom;


结晶器电磁搅拌电流对大方坯质量影响试验
2.
Simulating effects of electric current and molar of C to N on denitrification rates in biofilm of bio-electro reactor;
电流和碳氮的量比对生物电极脱氮速率影响的模拟
3.
Study on the Influence of Self-Consumable Electrode's End Shape by the Current in the Electroslag Casting Process;
电渣熔铸中电流对自耗电极端部锥角影响的研究
2) electric current


电流
1.
Heat sink project of big electric current in the low-temperature measurement;


低温大电流测量中热沉的设计
2.
Study on the distributions of electric current and heat in phosphorus furnace and its effect on the operation of the furnace
制磷电炉内电流、热量分布对制磷电炉运行的影响分析
3) electrical current


电流
1.
Parameters of Electrical Current and Speed Used in Thermal Error Prediction of Machining Center;
基于电流与速度参数的加工中心热误差预测方法
2.
Applying impeller cutting method to reduce circulation pump running electrical current;


叶轮切削法在降低热网循环泵运行电流中的应用
3.
Experimental study on the friction and wear behavior of 1Cr18Ni9Ti/copper-impregnated metallized carbon was carried out under the conditions of different loads,sliding speed and electrical current on a pin-on-disc tester.
在销-盘摩擦磨损试验机上试验了载荷、速度、电流对1Cr18Ni9Ti/浸金属碳对磨时的摩擦因数、磨损量及磨损形貌的影响。
4) A-currents


A-电流
5) direct current


直流电流
1.
Solidification behavior of alloy ZA27 under action of direct current;


ZA27合金在直流电流作用下的凝固行为
2.
Analysis on the causes of direct current fluctuation in rectifying system and the solutions;
整流系统直流电流波动原因分析及解决方案
3.
The influences of direct current density,heating temperature,and holding time on the microstructure evolution of magnesium alloy AZ91D during semi-solid isothermal heat treatment were studied,and the related mechanism was also discussed.
考察了直流电流密度、等温温度及等温时间对 AZ91D 镁合金半固态组织的影响,对电流影响组织演变的机理进行了探讨。
6) streaming current


冲流电流
1.
The calculation of streaming current induced by product oil flowing through pipeline is studied.
对成品油管道内油品流动所产生的冲流电流的计算进行了研究。
补充资料:电流
| 电流 electric current 电荷的定向流动。一般说来,产生电流的条件是,存在着可以移动的电荷和推动电荷移动的电场,两者缺一不可。在金属中,电荷的携带者(称为载流子)是自由电子;在电解液中,载流子是溶解在其中的酸、碱、盐等溶质分子离解成的正、负离子;在导电气体中,载流子是气体中的正、负离子和电子 ;在半导体中 ,载流子是电子和带正电的空穴。 就电荷移动所产生的各种效应而言,负电荷的移动等效于等量正电荷的反向移动。通常规定正电荷流动的方向为电流方向。 电流的强弱用电流强度I描述 。定义 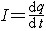 , 即电流强度(I)等于单位时间 (t)内通过导体任一横截面的电量(q)。I是标量,只能描述通过某一截面电流的整体特征 ,其单位为安培( A)。为了准确地描述各点电流的大小和方向,引入电流密度矢量j,其方向为正电荷流动的方向,其大小等于单位时间通过垂直于电荷流动方向的面积元dS的电流dI同面积元dS之比。其单位为安培/米2(A/m2)。 , 即电流强度(I)等于单位时间 (t)内通过导体任一横截面的电量(q)。I是标量,只能描述通过某一截面电流的整体特征 ,其单位为安培( A)。为了准确地描述各点电流的大小和方向,引入电流密度矢量j,其方向为正电荷流动的方向,其大小等于单位时间通过垂直于电荷流动方向的面积元dS的电流dI同面积元dS之比。其单位为安培/米2(A/m2)。在大块导体中,各点的电流分布形成的矢量场称为电流场。电流场可以用电流线来描绘和图示,电流线上每一点的切线方向即为该点电流密度矢量的方向,电流场中任一点的电流线的疏密则与该点电流密度的大小成正比。电流密度 j 和电流强度 I 的关系就是一个矢量场和它的通量的关系。 电流产生磁场。载流导线或运动电荷在磁场中受磁力作用。电流在导体中流动时会产生热。在电池或电解槽中,电流伴随着化学变化。电流的磁效应、机械效应、热效应、化学效应揭示了电现象与磁现象、力学现象、热现象、化学现象之间的联系,也提供了检验和量度电流的方法和手段。 导体中自由电荷在电场作用下的定向移动,电介质中极化电荷在变化电场作用下的移动,磁介质中分子电流在磁场作用下的定向分布所形成的电流,分别称为传导电流、极化电流和磁化电流。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条