1) black hole thermodynamics


黑洞热力学
1.
We introduce briefly the current situation and the issue of the research on black hole thermodynamics,and give the concept of black hole entropy and the theories related to black hole entropy,to discover the secret of dynamic black hole through steady black hole entropy and more information of star evolution.
简要介绍黑洞热力学的研究现状和存在的主要问题,给出了黑洞熵概念以及相关理论,目的通过稳态黑洞熵的提示探讨动态黑洞的秘密,更多地了解星体演变的信息。
2.
As two important projects in black hole thermodynamics, horizon and its surface gravity of black hole are directly related with the entropy of black hole and the temperature of radiation.
本文第一、二章简要回顾了黑洞热力学和η-ξ时空的主要内容。
2) laws of black hole thermodynamics


黑洞热力学定律
1.
Taking for an example the Reissner-Norstrom black hole, we reinvestigate its Hawking radiation of charged particles via tunneling, which is viewed from the laws of black hole thermodynamics.
以Reissner-Nordstrom黑洞(R-N黑洞)为例,从黑洞热力学定律出发,对R-N黑洞中的带电粒子的量子隧穿效应进行了重新分析。
3) the third law of thermodynamics of black hole


黑洞热力学第三定律
1.
The result obtained by studying black hole event horizon shows that the third law of therodynamics of black hole prohibits the naked singularity appearing;conversely,the naked singularity appearing must destroy the third law of thermodynamics of black hole.
对黑洞视界的研究结果表明 :黑洞热力学第三定律可禁止裸奇性的出现 ;反之 ,裸奇性的出现必破坏黑洞热力学第三定律。
4) Relation of black hole thermodynamics


黑洞热力学关系式
5) first law of black hole thermodynamics


黑洞热力学第一定律
1.
By adopting Parikh-Wilczek mode of quantum radiation as tunneling and first law of black hole thermodynamics,the tunneling effection of the general static spherically symmetric black hole is studied.
运用Parikh-Wilczek的量子隧穿模型和黑洞热力学第一定律研究一般静态球对称黑洞的Hawking辐射,得到了静止质量为零和不为零的粒子穿过黑洞事件视界的出射率具有完全相同的函数形式,发现粒子的量子隧穿辐射谱与黑洞的Bekenstein-Hawking熵变有关,辐射谱不再是严格的纯热谱。
6) black hole dynamics


黑洞动力学
补充资料:热力学:热力学第零定律
热力学第零定律:
热力学中以热平衡概念为基础对温度作出定义的定律。通常表述为﹕与第三个系统处於热平衡状态的两个系统之间﹐必定处於热平衡状态。图中A 热力学第零定律示意图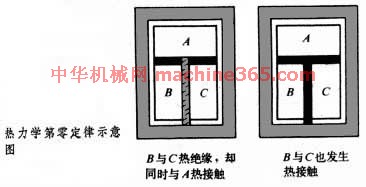 ﹑B 热力学第零定律示意图
﹑B 热力学第零定律示意图 ﹑C 热力学第零定律示意图
﹑C 热力学第零定律示意图  为 3个质量和组成固定﹐且与外界完全隔绝的热力系统。将其中的B ﹑C 用绝热壁隔开﹐同时使它们分别与A 发生热接触。待A 与B 和A 与C 都达到热平衡时﹐再使B 与C 发生热接触。这时B 和C 的热力状态不再变化﹐这表明它们之间在热性质方面也已达到平衡。第零定律表明﹐一切互为热平衡的系统具有一个数值上相等的共同的宏观性质──温度。温度计所以能够测定物体温度正是依据这个原理。
为 3个质量和组成固定﹐且与外界完全隔绝的热力系统。将其中的B ﹑C 用绝热壁隔开﹐同时使它们分别与A 发生热接触。待A 与B 和A 与C 都达到热平衡时﹐再使B 与C 发生热接触。这时B 和C 的热力状态不再变化﹐这表明它们之间在热性质方面也已达到平衡。第零定律表明﹐一切互为热平衡的系统具有一个数值上相等的共同的宏观性质──温度。温度计所以能够测定物体温度正是依据这个原理。
热力学中以热平衡概念为基础对温度作出定义的定律。通常表述为﹕与第三个系统处於热平衡状态的两个系统之间﹐必定处於热平衡状态。图中A 热力学第零定律示意图
 ﹑B 热力学第零定律示意图
﹑B 热力学第零定律示意图 ﹑C 热力学第零定律示意图
﹑C 热力学第零定律示意图  为 3个质量和组成固定﹐且与外界完全隔绝的热力系统。将其中的B ﹑C 用绝热壁隔开﹐同时使它们分别与A 发生热接触。待A 与B 和A 与C 都达到热平衡时﹐再使B 与C 发生热接触。这时B 和C 的热力状态不再变化﹐这表明它们之间在热性质方面也已达到平衡。第零定律表明﹐一切互为热平衡的系统具有一个数值上相等的共同的宏观性质──温度。温度计所以能够测定物体温度正是依据这个原理。
为 3个质量和组成固定﹐且与外界完全隔绝的热力系统。将其中的B ﹑C 用绝热壁隔开﹐同时使它们分别与A 发生热接触。待A 与B 和A 与C 都达到热平衡时﹐再使B 与C 发生热接触。这时B 和C 的热力状态不再变化﹐这表明它们之间在热性质方面也已达到平衡。第零定律表明﹐一切互为热平衡的系统具有一个数值上相等的共同的宏观性质──温度。温度计所以能够测定物体温度正是依据这个原理。
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条