1) standing wave protection ciruit
驻波保护电路
2) standing wave
驻波
1.
Research on vertical vector figure and standing wave;
旋转矢量图形与驻波问题的研究
2.
The discussion and computer dynamic simulation on traveling wave as the superposition of two standing waves;
两驻波叠加为行波的讨论及计算机动态模拟
3) Standing-wave
驻波
1.
Investigation on standing-wave thermoacoustically driven RC load with a pressure amplifier;
带压力放大器的驻波型热声发动机驱动RC负载
2.
Investigation on Performance of a Standing-wave Thermoacoustically Driven Pulse Tube;
驻波型热声驱动脉管制冷机性能研究
3.
Investigation on Performance Enhancement of a Standing-wave Thermoacoustic Engine;
驻波型热声发动机性能强化研究
4) standing waves
驻波
1.
Based on ABAQUS software,a FEM model about the standing waves in 215/55 R16 radial tire cord is constructed.
利用ABAQUS软件建立了较完整系统的轮胎驻波现象的有限元模型和分析方法,包括充气、加载、匀速滚动和加速滚动过程的有限元分析以及确定轮胎驻波临界速度的Euler描述和表征的方法。
2.
Which results in forming electron standing waves of concentric circles in the corral.
在金属表面上把电子约束在纳米尺度的环形量子围栏中,导致电子波在围栏内形成同心圆状的驻波。
3.
The Analysis of the standing waves on DLC channels is not involved in previous literature.
电力线信道的驻波分析是国内外文献很少涉及的课题。
5) stationary wave
驻波
1.
A measurement of sound speed by the method of stationary wave;
驻波法测量声波的传播速度
2.
This paper studies the law of sedimentation in the field of stationary wave,and investigates the formation mechanism of sand wave by a 2-D sedimentation model.
文章通过建立二维泥沙沉降模型,研究了驻波场中泥沙沉降的规律,对沙波的形成机理作了初步的探讨。
6) VSWR
驻波
1.
Effect of Amplifier VSWR on Performance of Direct Cascade Amplifer System;
在无隔离直接级联时放大器驻波对放大链系统性能的影响
2.
Its low attenuation, lower VSWR and perfect stability of impedance ensure this cable to be applied in many fields, such as cellular communication with analogic and digital system, broadcast, microwave, land mobile radio, military, etc.
这种电缆具有低损耗、低驻波、良好阻抗稳定性等优良性能。
7) clapotis
驻波
8) immobile wave
驻波
9) stationary waves
驻波
10) wave,standing
驻波
补充资料:驻波
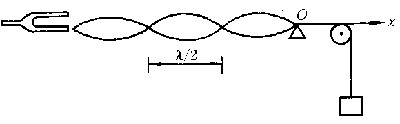
| 驻波 standing wave 频率和振幅均相同、振动方向一致、传播方向相反的两列波叠加后形成的波。波在介质中传播时其波形不断向前推进,故称行波;上述两列波叠加后波形并不向前推进,故称驻波。例如,如图所示,一弦线的一端与音叉一臂相连,另一端经支点O并跨过滑轮后与一重物相连。 音叉振动后在弦线上产生一自左向右传播的行波,传到支点O后发生反射,弦线中产生一自右向左传播的反射波,当弦长接近1/2波长的整数倍时。两列波叠加后弦线上各点的位移为(设音叉振动规律为u=Acosωt) u(x,t)=2Asin( 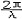 x)sin(ωt)=A(x)sin(ωt),弦线上每个固定的点均作简谐运动,但不同点的振幅不同,由x值决定。振幅为零的点称为波节,振幅最大处称为波腹。波节两侧的振动相位相反。相邻两波节或波腹间的距离都是半个波长。在行波中能量随波的传播而不断向前传递,其平均能流密度不为零;但驻波的平均能流密度等于零,能量只能在波节与波腹间来回运行。 x)sin(ωt)=A(x)sin(ωt),弦线上每个固定的点均作简谐运动,但不同点的振幅不同,由x值决定。振幅为零的点称为波节,振幅最大处称为波腹。波节两侧的振动相位相反。相邻两波节或波腹间的距离都是半个波长。在行波中能量随波的传播而不断向前传递,其平均能流密度不为零;但驻波的平均能流密度等于零,能量只能在波节与波腹间来回运行。测量两相邻波节间的距离就可测定波长。各种乐器,包括弦乐器、管乐器和打击乐器,都是由于产生驻波而发声。为得到最强的驻波,弦或管内空气柱的长度L必须等于半波长的整数倍,即 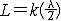 ,k为整数,λ为波长。因而弦或管中能存在的驻波波长为 ,k为整数,λ为波长。因而弦或管中能存在的驻波波长为 ,相应的振动频率为 ,相应的振动频率为 ,υ为波速。k=1时, ,υ为波速。k=1时,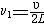 ,称为基频,除基频外,还可存在频率为kn1的倍频。 ,称为基频,除基频外,还可存在频率为kn1的倍频。
|
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条